System parameter identification
This tutorial displays a typical use case of optimization of control systems. The identification of parameters for a controller usually proceeds in the following steps:
- Data acquisition of the system to regulate in open loop
- Modeling the dynamic system
- Identification of the system parameters
- Set up of a control strategy (simple PID, to more evolve Model Predictive Control)
Example :
Second order system
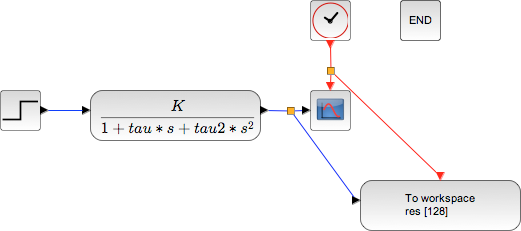
Running a simulation with a unit step input (with the parameters K, Tau et Tau2 all equals 1):
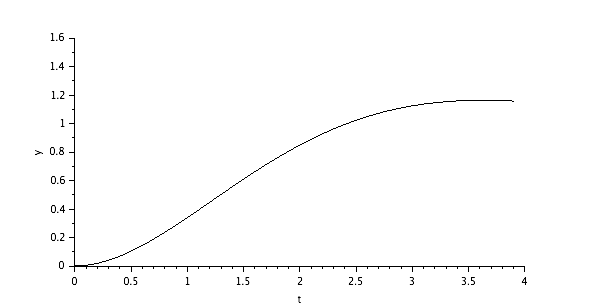
Introduction of the block “to workspace” to gather the results of the simulation in the Scilab environment for post-processing:
Those results are then accessible through the variable res, contening 2 fields :
- values
- time
Next step: Write an optimization script running Xcos in batch to identify the 3 parameters of the second order system (K, Tau and Tau2).
Defining a cost function returning y, the distance between the simulated curve of the system and the unit step input function.
function y=cost_for_fminsearch(x)
context = ["K="+string(x(1)) "tau="+string(x(2)) "tau2="+string(x(3))];
// On impose un cout infini si on sort de nos bornes de recherche.
if x(1) < 0 | x(2) < 0 | x(3) < 0 then
y=%inf
return
end
try
// Ouverture du diagramme => cree une variable scs_m
importXcosDiagram(pwd()+"/Asserv_2nd_ordre.zcos");
// Changement du contexte
scs_m.props.context = context;
// Simulation
xcos_simulate(scs_m, 4);
catch
disp("Error during xcos Simulation ...");
error("cost function failed.")
y = %inf;
return
end
res_ref = ones(40,1);
y = norm(res.values - res_ref)^2;
e = get("costPolyline");
e.data(:, 2) = res.values;
endfunction
The results are represented dynamically from this script iterating until finding the optimal solution in the defined interval:
f = gcf(); plot([0, 3.9], [1, 1], "r"); plot([0:0.1:3.9], zeros(40, 1)); e = gce(); e.children(1).tag = "costPolyline"; a = gca(); a.data_bounds = [0, 0 ; 4, 1.8]
The optimization function called to identify the 3 systems parameters is fminsearch :
opt = optimset( "Display" , "iter" ); [x fval] = fminsearch ( cost_for_fminsearch , [0 0 0] , opt );
The calling syntax of this function is:
- Cost function defining the quantity to minimize:
cost_for_fminsearch - Starting point of the search:
[0 0 0] - Advanced options with the function optimset:
options.Display = "iter" → the algorithm returns a message at each iteration
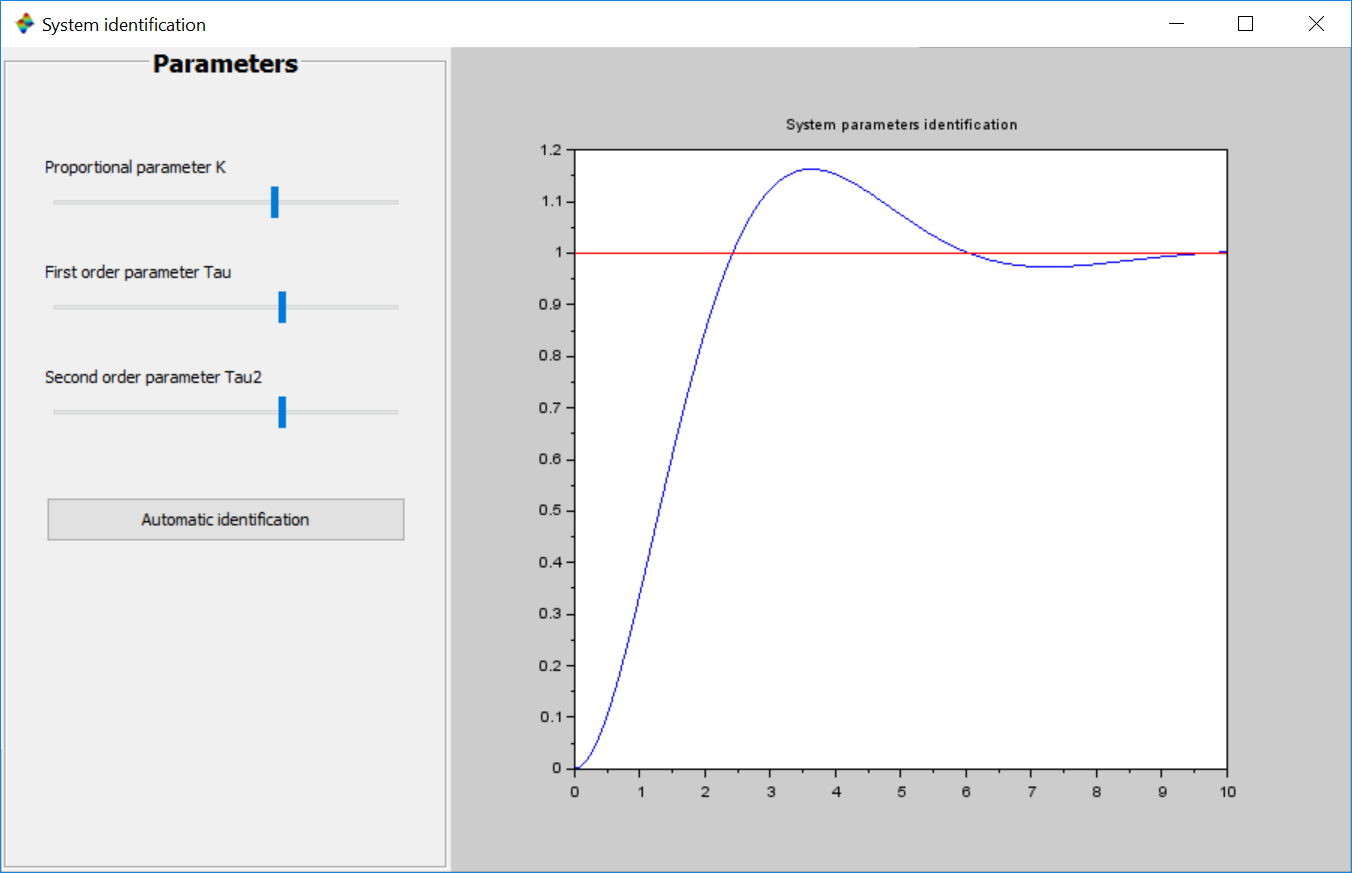
You can develop a Graphical User Interface (GUI) to modify manually the 3 parameters or trigger the automatic identification. Read the following tutorial to find out how.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.